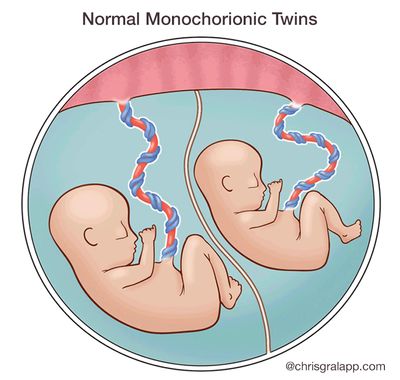
What are monochorionic twins?
A single placenta normally supports a single fetus. When the situation arises in which two fetuses have to share a single placenta, complications may sometimes develop. Identical twins that share a single placenta are called monochorionic twins (MC). “Chorion” is the Latin root that refers to the placenta, while the word “amnion” refers to the sac, or “membranes” that surround each fetus. While fraternal twins (2 eggs and 2 sperm) are always surrounded in their own sacs and have their own individual placentas, 70% of identical twins may end up sharing a single placenta. Only 1% of identical twins share both a single placenta and a single sac, and this poses significant risk.
When two fetuses share one placenta, their umbilical cords may implant anywhere – there is no set or predictable pattern – and depending on where they implant, one fetus may get less of a ‘share’ of the placenta than it’s co-twin, resulting in less blood flow and nutrition to one fetus, with more to the other (unequal placental sharing). As a result, although identical twins usually share the same genetic material, they may actually grow differently. Like the roots of a tree, the blood vessels that run from each implanted cord may connect with each other beneath the surface, as there is nothing separating them within a single placenta. Depending on which types of vessels connect to which, one fetus may transfuse blood to the other. We will discuss each of these complications, their risks, and potential treatments, below.
Monochorionic Twins Recommendations
The following recommendations are meant for both patients and their providers as guidance during a pregnancy with monochorionic twins. For questions and referrals please call us at 1-800-RX-FETUS.
You can also download and print this information with our Monochorionic Twins Recommendations PDF brochure.
Complications Unique to Monochorionic Twins
- Unequal placental sharing
- Selective intrauterine growth restriction (S-IUGR) in one fetus
- TTTS - clinically defined as a deepest vertical pocket of > 8 cm in one twin and > 2 cm in in the other twin, simultaneously; TTTS can be seen overlapping with growth discordance, but these are separate diagnoses with different pathophysiologies
- Twin anemia polycythemia sequence (TAPS)
- Non-TTTS amniotic fluid discordance
- Discordant anomalies
- TRAP Sequence
Components of UCSF Evaluation
- Level II anatomic survey for (discordant) fetal anomalies
- Special attention paid to cord insertion locations and vascular mapping
- Fetal echocardiography for structural and functional integrity
- Fetal brain MRI > 22 weeks when indicated and appropriate
Potential Surgical Procedures
- Selective fetoscopic laser ablation
- Radiofrequency ablation (RFA) for cord occlusion
Timeframe for Referrals to UCSF
We welcome your call at any time to discuss your findings and obtain guidance about timing for referral and level of urgency 1-800-RX-FETUS.
Consider Referral
- Significant amniotic fluid discordance
- Significant growth discordance (>20 percent)
- Isolated abnormal Doppler results
- Suspected discordant anomaly
Unless there is a lethal anomaly, if possible refer prior to 24 weeks to retain the option of RFA.
We encourage you to call our center to discuss your findings if you have concerns at 1-800-RX-FETUS
Call for Timely Referral (need to see patient within 1 week)
- Concurrent DVPs >8 cm and >2 cm, with normally sized bladder visualized and normal umbilical arterial (UA) Doppler results.
Call for Urgent Referral (need to see patient within a couple days)
- Concurrent DVPs >8 cm and >2 cm and either no visible donor twin bladder, abnormal UA Doppler results, suspected recipient cardiomyopathy or hydrops.
What is Needed For Referral
Patients referred to UCSF for an evaluation should have the following faxed to 415-502-0660:
-
Demographic information
-
A copy of the front/back of their health insurance card
-
All obstetric/maternal-fetal medicine (OB/MFM) medical records
-
If insurance authorization is required, for proper codes please download the Monochorionic Evaluation Codes.
-
Afterwards, call 1-800-RX-FETUS or 1-800-793-3887 to discuss your patient and complete the referral process.